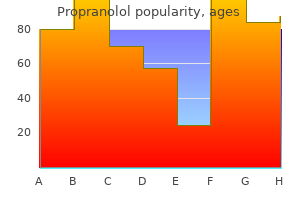
Propranolol
"Discount propranolol 80 mg on line, cardiovascular nutrition".
H. Redge, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Co-Director, Alpert Medical School at Brown University
Glucose and insulin will also shift K into cells to temporarily lower serum K levels blood vessels in spanish order propranolol 80mg on-line. Furosemide can be given for kaliuresis as well as natiuresis if volume expansion is present cardiovascular disease xyy propranolol 40mg low price. Dialysis is considered when hyperkalemia cannot be controlled with medical therapy cardiovascular system organ functions cheap propranolol 40 mg without a prescription. Unless dehydration or polyuric states are present cardiovascular disease african american generic propranolol 20 mg amex, volume should be limited to replacement of insensible losses and urine output (see Chap. The inability to adequately prescribe nutrition due to fluid restriction and/or significant fluid overload are indication for dialysis. Sodium (Na) is restricted and Na concentration is monitored, accounting for fluid balance. Close monitoring of electrolytes especially sodium is needed during diuretic therapy or with dialysis. Calcium supplementation is given if ionized calcium is decreased or the patient is symptomatic. In infants with chronic renal failure, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D or its analog is given to maximize Ca2 absorption and prevent renal osteodystrophy (see Chap. Metabolic acidosis is usually mild, unless there is (i) significant tubular dysfunction with decreased ability to reabsorb bicarbonate, or (ii) increased lactate production due to decreased perfusion due to heart failure or volume loss from hemorrhage (see I. Consider using sodium bicarbonate or sodium citrate to correct severe metabolic acidosis. Infants who can take oral feeding are given a low-phosphate and low-potassium formula with a low renal solute load. Caloric density can be progressively increased to a maximum of 50 kcal/oz with glucose polymers (Polycose) and oil. Adequate protein for neonates with otherwise normal renal function should be provided unless they are on continuous hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Dialysis is indicated when conservative management has been unsuccessful in correcting severe fluid overload, hyperkalemia, acidosis, and uremia. Inadequate nutrition because of severe fluid restriction in the anuric infant is a relative indication for dialysis. Because the technical aspects and the supportive care are specialized and demanding, this procedure must be performed in centers where the staff have experience with dialysis in infants and neonates. The severity of renal impairment in these diseases varies from extreme oligohydramnios and in utero compromise to late presentation in Fluid Electrolytes Nutrition, Gastrointestinal, and Renal Issues 367 adulthood. Ultimately, the prognosis depends on the severity of the anomaly, whether the contralateral kidney is viable and on extrarenal organ dysfunction. In the newborn course, the degree of pulmonary hypoplasia will dictate the likelihood of viability. Blood pressure rises with postnatal age, 1 to 2 mm Hg/day during the first week and 1 mm Hg/week during the next 6 weeks in both the preterm and full-term infant. Normative values of blood pressure for full-term infants and premature infants are shown in Tables 28. Hypertension is defined as persistent blood pressure 2 standard deviations above the mean. The three most common causes of hypertension in newborns are secondary to bronchopulmonary dysplasia, umbilical artery thrombus emboli, and coarctation of the aorta. History and physical examination, a review of fluid status, medications, location of arterial thrombus, and weak distal pulses, may provide clues about the underlying etiology. Renin-mediated hypertension and fluid overload may both contribute to renal causes of hypertension. Urinalysis, renal function studies, serum electrolyte levels, and renal ultrasonographic examination should also be obtained. Color Doppler flow studies may detect aortic or renal vascular thrombosis, although this test is not reliable with the possibility of both false positives and false negatives. Echocardiogram is indicated if coarctation is suspected and can determine if left ventricular hypertrophy has occurred from sustained hypertension. Other rare causes include congenital hypercoagulable states and severe hypotension. While the management is controversial, potential options include surgical thrombectomy, thrombolytic agents, and conservative medical care, including antihypertensive therapy.
Low-risk patients do not return for further screening as their risk of a fetus with Down syndrome is low heart disease early symptoms propranolol 80 mg overnight delivery. When the two types of sequential tests are compared heart disease zinc generic 20 mg propranolol fast delivery, they have similar overall screen positive rates of 2% to 3% heart disease untreated cheap propranolol 80mg online, and both have sensitivities of over 90% for trisomy 21 (stepwise arteries yahoo 80mg propranolol, 95%; contingent, 93%). Secondtrimester ultrasound targeted for detection of aneuploidy has been successful as a screening tool. Application of second-trimester ultrasound that is targeted to screen for aneuploidy can decrease the a priori maternal age risk of Down syndrome by 50% to 60%, as well as the risk conveyed by the second-trimester serum screening. Recently, second-trimester ultrasound following first-trimester screening for aneuploidy has likewise been shown to have value in decreasing the risk assessment for trisomy 21. In women with a positive family history of genetic disease, a positive screening test, or at-risk ultrasonographic features, diagnostic tests are considered. When a significant malformation or a genetic disease is diagnosed prenatally, the information gives the obstetrician and pediatrician time to educate parents, discuss options, and establish an initial neonatal treatment plan before the infant is delivered. Under ultrasonic guidance, a sample of placental tissue is obtained through a catheter placed either transcervically or transabdominally. Direct preparations of rapidly dividing cytotrophoblasts can be prepared, making a full karyotype analysis available in 2 days. Although direct preparations minimize maternal cell contamination, most centers also analyze cultured trophoblast cells, which are embryologically closer to the fetus. Amniotic fluid is removed from around the fetus through a needle guided by ultrasonic images. In cases of isoimmune hemolysis, increased levels of bilirubin in the amniotic fluid reflect erythrocyte destruction. Amniotic fluid bilirubin proportional to the degree of hemolysis is dependent upon gestational age and can be used to predict fetal well-being (Liley curve) (see Chap. Pulmonary surfactant can be measured once or sequentially to assess fetal lung maturity (see Chap. Fetal cells can be extracted from the fluid sample and analyzed for chromosomal and genetic makeup. Among second-trimester amniocentesis, 73% of clinically significant karyotype abnormalities relate to one of five chromosomes: 13, 18, 21, X, or Y. An anterior placenta facilitates obtaining a sample close to the cord insertion site at the placenta. Early in gestation (at the eight-cell stage in humans), one or two cells can be removed without known harm to the embryo. Similarly, woman at increased risk for a chromosomally abnormal conception can benefit from preimplantation biopsy. When one member of a couple carries a balanced translocation, only those embryos that screen negative for the chromosome abnormality in question are transferred. An alternative approach is analysis of the second polar body, which contains the same genetic material as the ovum. Whereas fetal cells in the maternal circulation can be separated and analyzed to identify chromosomal abnormalities, the limited numbers preclude using this technique on a clinical basis. Development of a noninvasive method of prenatal diagnosis is ideal because it would eliminate the potential procedure-related loss of a normal pregnancy. Development of modalities to address the intricacies of the ratios involved in assessing aneuploid conditions is rapidly evolving. Further work is needed to determine the most appropriate signal to sort the smaller fetal fragments of free nucleic acids from the larger body of maternal-free nucleic acids. Appropriate fetal assessment is important in establishing a diagnosis and a perinatal treatment plan. It is important to identify constitutionally normal fetuses whose growth is impaired so that appropriate care can begin as soon as possible. Once delivered, these newborns are at increased risk for immediate complications including hypoglycemia and pulmonary hemorrhage, so they should be delivered at an appropriately equipped facility. Prenatal diagnosis of malformed or infected fetuses is important so that appropriate interventions can be made. Strictly speaking, any fetus that does not reach his or her intrauterine growth potential is included. Clinical diagnostics detect about two-thirds of cases and incorrectly diagnose it about 50% of the time.
Ablative techniques Microwave) (Radiofrequency heart disease online test generic propranolol 20mg without a prescription, Cryosurgery blood vessels 3d printing purchase 20mg propranolol overnight delivery, Alcohol injection cardiovascular kansas city generic propranolol 80 mg with mastercard, B cardiovascular careers order propranolol 80mg. For select lesions, generally under 3 cm in size that are well localized, definitive treatment may be considered. Local control rates in the range of 90% at two years have been reported for ablative techniques. Radiation Therapy Criteria these techniques require selective catheterization of the hepatic arterial supply to the tumor-involved liver segments. Indications for these procedures include multiple tumors, generally 4 or more in number, lesions greater than 3 to 5 cm, lesions without vascular invasion or extra-hepatic spread. Relative contraindications include tumor size greater than 10 cm, severe cardiovascular or pulmonary disease, varices at high risk of bleeding or bile duct occlusion. The University of Michigan has demonstrated that tumoricidal doses from 40 Gy to 90 Gy delivered in 1. The unique dosimetric advantages of heavy charged particle radiation (Bragg Peak) offer significant potential advantages in sparing hepatic parenchyma compared to traditional photon techniques. This theoretical advantage is still the object of on-going studies in this country. A consultation note from Interventional Radiology documenting the contraindications as listed above to the use of ablative or transarterial techniques and 2. There were no significant differences between the groups with each group receiving 70 Gy. On bivariable analysis, increased mean oral cavity dose was associated with a higher rate of G-tube placement; no patient required a G-tube if the mean oral cavity dose was < 26 Gy whereas all patients with a mean dose of > 41. In an analysis of toxicity, charged particle therapy was found to be significantly associated with more neurological toxic effects (p = 0. Sixteen patients (32%) required evaluation in an emergency room during treatment with 10 subsequently requiring hospitalization primarily due to dehydration and pain from mucositis. It was noted that patients receiving a G-tube during radiotherapy had significantly longer history of smoking, greater comorbidity, more advanced disease, greater need for bilateral treatment, higher use of induction chemotherapy and concurrent chemotherapy, and a longer duration of treatment. Sites of treatment included the larynx (1), nasopharynx (5), paranasal sinus (2) and oropharynx (1). At a median follow up of 27 months, four patients (44%) achieved a complete response, four achieved a partial response without disease progression and one developed local progression. This heterogeneous group of patients included 19 receiving treatment at initial diagnosis and seven receiving treatment at recurrence (six of whom had prior radiation and three of whom had pulmonary metastases). Longer follow-up is needed to gauge the durability of disease control and to monitor for late toxicities of therapy. Sites of treatment included lacrimal gland or sac (5), paranasal sinus (4), parotid gland (4), submandibular gland (2) and buccal mucosa (1). Median dose delivered was 60 Gy with 12 patients receiving concurrent chemotherapy. Four patients developed acute grade 3 toxicity and one patient experienced a grade 4 toxicity (blindness). An additional patient developed asymptomatic frontal lobe necrosis 18 months after treatment completion with near resolution at 24 months. Primary sites included the lacrimal gland (7), lacrimal sac/nasolacrimal duct (10) or eyelid (3). Seven patients experienced acute grade 3 while 9 patients developed chronic grade 3 ocular or eyelid function toxicity. Bivariate analysis revealed that a dose of 36 Gy or less to the ipsilateral cornea was associated with grade 3 chronic ocular toxicity (p = 0. Additional data are needed to identify which patients are most likely to benefit from aggressive efforts to achieve local disease control and to evaluate the potential benefit of proton therapy relative to other modalities of reirradiation.

A discussion of their physical and chemical properties heart disease risk calculator 40 mg propranolol free shipping, their routes of entry cardiovascular genetics buy propranolol 20mg with amex, and descriptions of symptoms is also provided physiology cardiovascular system youtube generic propranolol 20 mg with mastercard. Nerve agents acquired their name because they affect the transmission of impulses in the nervous system cardiovascular system the heart chapter 11 order propranolol 40mg with amex. All nerve agents belong to the chemical group of organophosphorus compounds; many common herbicides and pesticides also belong to this chemical group. Nerve agents are stable, easily dispersed, highly toxic, and have rapid effects when absorbed both through the skin and the respiratory system. Uptake is mainly through the skin but also through inhalation of the substance as a gas or aerosol. A highly volatile (nonpersistent) substance poses a greater respiratory hazard than a less volatile (persistent) substance. Table 3-1 lists the common nerve agents and some of their physical and chemical properties. Poisoning may also occur through consumption of liquids or foods contaminated with nerve agents. The route of entry also influences the symptoms developed and, to some extent, the sequence of symptom onset. Since nerve agents are somewhat fat-soluble, they can easily penetrate the outer layers of the skin, but it takes longer for the poison to reach the deeper blood vessels. Consequently, the first symptoms do not occur until 20 min to 30 min after the initial exposure but subsequently, the poisoning process may be rapid if the total dose of nerve agent is high. In addition, the capacity of the eye to change focal length is reduced, and short-range vision deteriorates causing the victim to feel pain when trying to focus on nearby objects. Exposure to a moderate dose leads to more dramatic developments, and symptoms are more pronounced. Bronchoconstriction and secretion of mucus in the respiratory system lead to difficulty in breathing and to coughing. Discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract may develop into cramping and vomiting, and there may be involuntary discharge of urine and feces. If the poisoning is moderate, typical symptoms affecting the skeletal muscles may be muscular weakness, local tremors, or convulsions. When exposed to a high dose of nerve agent, the muscular symptoms are more pronounced, and the victim may suffer convulsions and lose consciousness. The poisoning process may be so rapid that symptoms mentioned earlier may never have time to develop. This section provides an overview of blister agents, including a discussion of their physical and chemical properties, their routes of entry, and descriptions of their symptoms. Given the similarity of their physiological effects, the traditional blister agents and the arsenical vesicants are discussed together in this section. All blister agents are persistent and may be employed in the form of colorless gases and liquids. Blister agents are likely to be used to produce casualties rather than to kill, although exposure to such agents can be fatal. Supportive care for blister agent casualties is often manpower and logistically intensive. They have a faint odor of mustard, onion, garlic, or horseradish, but because of olfactory fatigue, odor cannot be relied on for detection. At room temperature, mustard agent is a liquid with low volatility and is very stable during storage. Mustard agent can be easily dissolved in most organic solvents but has negligible solubility in water. In aqueous solutions, mustard agent decomposes into nonpoisonous products by means of hydrolysis but since only dissolved mustard agent reacts, the decomposition proceeds very slowly. Oxidants such as chloramines, however, react rapidly with mustard agent, forming nonpoisonous oxidation products.